Overview
Cloud Requests can be divided in two categories Control-Plane and Data-Plane.
Control-Plane
These APIs are used to create and manage cloud resources within a specific tenant. The Control Plane APIs handle the lifecycle of resources and provide configuration details such as metadata, properties, and state information. All resources managed through the Control Plane APIs adhere to a standardized resource schema.
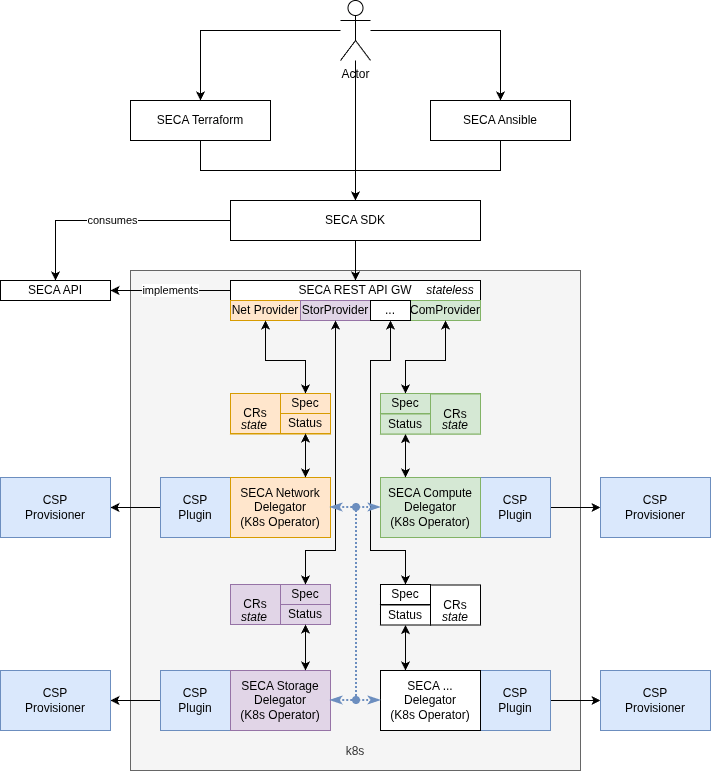
A key component of the SECA architectural model is the SECA REST API Gateway, which provides users and customers a standard way to interact with SECA resources across all Cloud Service Providers (CSPs).
The API Gateway relies on Kubernetes Custom Resources (SECA CRs) to represent and store the state of SECA resources. In response to API calls, the Gateway writes the desired state to the CR's Spec section and reads the actual state from its Status section.
These SECA CRs are managed by SECA Delegators, which are Kubernetes Controllers that reconcile the resources. The Delegators detect changes to a CR's Spec and trigger the appropriate actions on the CSP to achieve the desired state. They are also responsible for updating the CR's Status field when responses are received from the CSPs.
Delegators do not interact directly with CSPs; instead, they use CSP Plugins. A Plugin acts as the first translation layer, providing a set of common interfaces and their specific implementation for a particular CSP.
The Plugins enable the Delegator to interact with the CSP Provisioner — the native mechanism the CSP provides to allow the SECA machinery to manage resources on its platform.
Data-Plane
When interacting with cloud resources, Data Plane operations are directed to instance-specific endpoints, allowing direct access to the underlying data and services, such as object storage or databases. The primary role of Data Plane APIs is to handle and return data, whether in the form of files, query results, or responses to data manipulation requests.
Because Data Plane services span a wide range of technologies — including NFS, SQL, key/value stores, and vaults — their API schemas naturally vary. Unlike Control Plane APIs, which focus on metadata and configuration, Data Plane APIs operate exclusively on the actual data, supporting its retrieval, manipulation, and delivery.
As a result, Data Plane APIs serve a distinct purpose within the cloud ecosystem and remain outside the scope of the SECA API.
Control Plane vs Data Plane
Control Plane APIs
Control Plane APIs are responsible for managing the lifecycle, configuration, and metadata of cloud resources.
They provide a unified, provider-agnostic interface through the SECA API, ensuring consistency across environments.
- Primary Role: Manage resources (create, update, delete) and return configuration details such as metadata, properties, and states.
- Endpoints: Common API server shared across providers.
- Schema: Standardized resource schema.
- Examples:
- Create a VM instance
- Configure a network
- Assign roles or policies
Data Plane APIs
Data Plane APIs handle direct interaction with data and services provisioned by cloud resources.
They operate at the instance level and are not part of the SECA API, as their schemas vary by service type.
- Primary Role: Operate on actual data (read, write, query, manipulate).
- Endpoints: Instance-specific service endpoints.
- Schema: Variable schemas depending on service type (e.g., NFS, SQL, Key/Value, Vaults).
- Examples:
- Upload/download files from object storage
- Execute SQL queries on a managed database
- Read/write key-value pairs
- Retrieve secrets from a vault
Summary Table
| Aspect | Control Plane APIs | Data Plane APIs |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage lifecycle, configuration, and metadata of resources | Operate directly on data and services |
| Endpoints | Common, provider-agnostic API server | Instance-specific service endpoints |
| Focus | Metadata, resource properties, and states | Files, query results, objects, and responses to data operations |
| Schema | Standardized resource schema (consistent across providers) | Variable schemas (depends on service type: NFS, SQL, Key/Value, Vaults, etc.) |
| Integration | Unified under SECA API | Outside SECA API scope |
| Examples | Create VM, configure network, assign roles | Upload/download files, execute SQL queries, read/write key-value pairs |